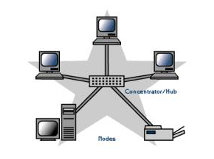
Wired Networks
Wired
networks, also called Ethernet networks, are the most common type of
local area network (LAN) technology. A wired network is simply a
collection of two or more computers, printers, and other devices
linked by Ethernet cables. Ethernet is the fastest wired network
protocol, with connection speeds of 10 megabits per second (Mbps) to
100 Mbps or higher. Wired networks can also be used as part of other
wired and wireless networks. To connect a computer to a network with
an Ethernet cable, the computer must have an Ethernet adapter
(sometimes called a network interface card, or NIC). Ethernet
adapters can be internal (installed in a computer) or external
(housed in a separate case). Some computers include a built-in
Ethernet adapter port, which eliminates the need for a separate
adapter.
Wireless Networks
A wireless
network, which uses high-frequency radio waves rather than wires to
communicate between nodes, is another option for home or business
networking. Individuals and organizations can use this option to
expand their existing wired network or to go completely wireless.
Wireless allows for devices to be shared without networking cable
which increases mobility but decreases range. There are two main
types of wireless networking; peer to peer or ad-hoc and
infrastructure.
An ad-hoc or
peer-to-peer wireless network consists of a number of computers each
equipped with a wireless networking interface card. Each computer can
communicate directly with all of the other wireless enabled
computers. They can share files and printers this way, but may not be
able to access wired LAN resources, unless one of the computers acts
as a bridge to the wired LAN using special software.
An infrastructure
wireless network consists of an access point or a base station. In
this type of network the access point acts like a hub, providing
connectivity for the wireless computers. It can connect or bridge the
wireless LAN to a wired LAN, allowing wireless computer access to LAN
resources, such as file servers or existing Internet Connectivity.
Wired Networks
|
|
|---|---|
| Pros | Cons |
|
|
Wireless Networks
|
|
|---|---|
| Pros | Cons |
|
|


No comments:
Post a Comment